Cathrine's deep connection to Malawi is so inspiring
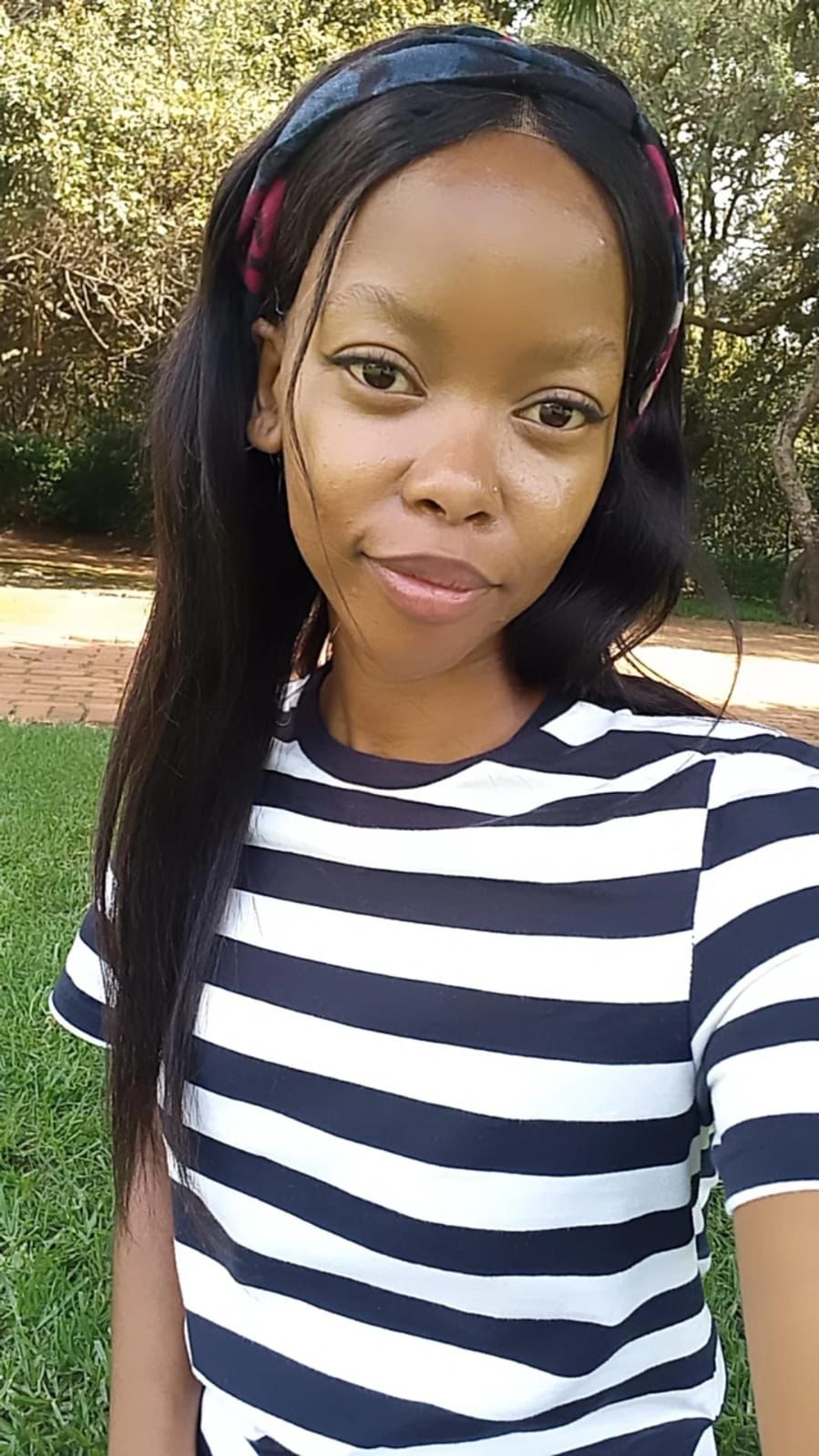
Meet Cathrine, a young Malawian woman who was born and raised in Zimbabwe. Despite growing up far away from her ancestral land, Cathrine was always drawn to Malawi and its beautiful landscapes. As a child, she dreamt of one day visiting her parent's homeland, and when she finally did, it was love at first sight. She was captivated by the lush greenery, cultivated fields, the rolling green hills, and the friendly, welcoming people of traditional rural African villages. 
Cathrine's connection to Malawi deepened over time, even as she faced various social and financial challenges that forced her to leave her country. She never forgot the warmth and kindness of the people she had met there, and she remained committed to helping them in any way she could. 
In 2021, Cathrine finally returned to Malawi to settle in her parents' village of Tukombo, located in the Northern region where the Tonga-speaking people reside. She was eager to reconnect with her roots and to make a positive impact on her community. She reached out to the Traditional Authority (TA) of the village's land to understand the most pressing needs in the area, and she was determined to find a way to help, even though she had no resources of her own.
Cathrine's unwavering dedication to her community inspired her to seek out like-minded friends who shared her vision of creating a better Africa for present and future generations. Together, they embarked on a journey of asking for assistance, and Cathrine was humbled by the overwhelming response from her friends, who were eager to help her build her village and work towards creating a better Africa, one village at a time. Despite having limited resources, Cathrine was able to make a significant impact on the lives of those in need in her village by providing assistance and support whenever needed. 
Cathrine's passion for the environment led her to get involved in a tree-planting project in her community of Tukombo. She collaborated with Chifundo from the DFFE, and together, they planted trees in a school and an elderly home. Cathrine had to seek permission from the Chief, Zilakoma - Mr Wellington, to run the project on their land, and he was eager to assist Cathrine in carrying out her vision to transform the landscapes while preserving the cultures and traditions that her ancestors had worked so hard to build. Her approach to the tree-planting project was unique and inspiring. She not only taught pupils how to plant trees but also explained why it was important and how to care for them. She encouraged each student to plant trees with a purpose and to name each tree they planted so they could nurture and protect it as a living treasure. Cathrine's dedication to planting trees and helping those in need is truly admirable. Her efforts have given hope for the future of our planet and the natural world. Her story is a testament to the fact that one person can make a significant difference in their community with determination and a clear vision.
Naledi’s Story On Navigating Mental Health Challenges And Finding Purpose
Sometimes, we suffer in silence. I started having mental health issues at a young age, not knowing what they were exactly, and in turn, they formed part of my personality. These mental health issues then started being apparent in my early adult years; they were a manifestation of all my childhood traumas. I learned that I had depression and anxiety when I went to varsity and did more research on what I was going through.
I found that I had all the symptoms: I had no desire to live, I had given up and struggled with being in social situations and articulating what I wanted or needed, and I was very withdrawn and always very negative-minded. Because I was quiet, my mind was a dangerous place to live in. I then attempted to commit suicide with failure. I had a support system that tried their best to help me overcome this even though they didn’t understand what I was going through.
As time went on, I then started to read self-help books because I was tired of living in constant pain. I didn’t want to survive; I wanted to live. I drove myself out of the pit of depression even though it was a very long and tough battle. Today, I am happy I get to tell my story. There’s a lot that people go through and never get assistance or even self-help. Mental health issues are a very vital part of our overall health as they distort views of an individual in so many ways. It is important to keep healthy habits for our mental health so we can not only live but thrive.
If I were to offer advice to someone going through similar mental health challenges, my primary suggestion would be to find the root cause of their distress because mental health challenges often stem from deeper, underlying issues. Identifying what specifically triggers your emotional responses and understanding the reasons behind these triggers are crucial steps. Uncovering the ‘whys’ paves the way to addressing and resolving the core issues at hand. While this approach may prove beneficial for some, it’s important to acknowledge that it might not be effective for everyone.
Moreover, it’s important to allow yourself to experience and process your emotions fully – but refrain from acting impulsively on negative thoughts, as such actions can be harmful and sometimes even worse. Allowing yourself the space to express feelings such as sadness or anger is very important for releasing stress. For those who find it difficult to express emotions openly, journaling could be a helpful option.
Above all, if you’re struggling with mental health issues, I think it is important to be kind to yourself more than anything. Practice self-love through doing things that make you feel alive and happy. This helped me to find myself again and to find purpose in little things.
The African woman whose legacy has changed my life: Wangari Maathai
This is the story of the African woman who made me love the environment. Her story inspired me to pursue a career in environmental and climate justice, and it also inspired me to pursue my dreams, irrespective of the societal limitations placed on my skin colour and gender.
Wangari was born in Kenya on April 1st, 1940, during British colonial rule. Her family was of Kikuyu origin, and her father was polygamous. As a child, Wangari, was given a small plot of land to grow her own food and to learn how to cultivate the land. She completed her primary and secondary education in Kenya. In 1960, she received a scholarship to commence her university studies in the United States of America, where she received a Bachelor's and a Master's degree in Biological Sciences. In April 1966, after returning to Kenya, Wangari met her future husband, Mwangi Mathai, a politician. The two got married in May 1969.
From 1966 to 1982, Wangari Maathai was a lecturer at the University of Nairobi, and in 1971, Wangari received her Doctorate in Veterinary Anatomy from the University of Nairobi, becoming the first woman in eastern Africa to receive a PhD.
 In 1977, Wangari and her husband got divorced. Soon after that, Wangari was imprisoned because she publically contested the judge's ruling regarding her divorce. As this ruling was in favour of her ex-husband and it shamed her for being a woman in need of a divorce. As a result, the judge ordered her to stop using her former husband's last name. In defiance of the judge, she changed the spelling of her last name, adding an "a" and becoming Wangari Maathai. That same year, she founded the Green Belt Movement. This grassroots environmental non-governmental organization planted over 30 million trees across Kenya over the next three decades. This movement became a successful platform for women's empowerment (especially for rural women in Kenya). As a result, she became known as Africa's Mother of Trees.
In 1977, Wangari and her husband got divorced. Soon after that, Wangari was imprisoned because she publically contested the judge's ruling regarding her divorce. As this ruling was in favour of her ex-husband and it shamed her for being a woman in need of a divorce. As a result, the judge ordered her to stop using her former husband's last name. In defiance of the judge, she changed the spelling of her last name, adding an "a" and becoming Wangari Maathai. That same year, she founded the Green Belt Movement. This grassroots environmental non-governmental organization planted over 30 million trees across Kenya over the next three decades. This movement became a successful platform for women's empowerment (especially for rural women in Kenya). As a result, she became known as Africa's Mother of Trees.
Wangari was imprisoned several times in the 1980s for criticizing Kenyan President Daniel Arap Moi and for demanding multi-party elections in Kenya. She stood for environmental justice due to new construction developments that endangered the environment and indigenous peoples' rights. Furthermore, in 1992, Maathai ran for president on a platform urging environmental protections. And at that time, she was the first African politician to embrace that cause publicly. She withdrew from the elections but ran again in 1997. In 2003, she founded the Mazingira Green Party of Kenya and later that year, she was appointed Assistant Minister for Environmental and Natural Resources by Kenyan President Mwai Kibaki. 
In 2004, Maathai won the Nobel Prize for her work in protecting the environment through political lobbying and reforestation initiatives. These initiatives were aimed at empowering rural women in Kenya. This was an outstanding award as it's prestige helped put environmental rights on the map.
In 2006, she was one of the founders of the Nobel Women's Initiative, an organization of six women recipients of the Nobel Prize, representing North and South America, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, who united in their efforts to work for peace, justice, and equality throughout the world. In January 2007, Maathai hosted the Global Young Greens conference in Nairobi, which some have described as a meeting of the next wave of the leadership of the world environmental movement. In addition, Maathai wrote four books, including "The Greenbelt Movement: Sharing the Approach and the Experience".
At 71, Wangari Maathai died from complications from ovarian cancer treatment at a Nairobi hospital.
But her legacy lives on!
Today millions of women like myself have gained inspiration from her story and aim to share this story with many people. Her passion, resilience and approach to environmental rights and gender equality contributed significantly to my career path. I am forever grateful!
Source for refernace:
The founder of the Green Belt Movement and the 2004 Nobel Peace Prize Laureate
Photo 1 and photo 2 credit: Pinterest
When climate change impacts African women, it also affects me as an African woman
My name is Ms Rosemary Olive Mbone Enie. I am a Cameroonian Geologist, Environmentalist, Social Environmental Entrepreneur (SEE), Eco-communities Builder, Gender and Childhood Ambassador. I was born on the 27th August 1966 in Victoria South West Region of Cameroon.
Victoria, now called Limbe, is a seaside town by the banks of the Atlantic Ocean. While growing up, we had several clean flowing rivers, which took its source of the ranges of the majestic Mount Cameroon through the rocky volcanic terrain into the Atlantic Ocean. Back in the youthful days' rainfall was stable, farmers had specific reasons to plant their crops, and the yields were moderate. The town of Victoria (Limbe) was full of trees and plantations of Oil Palm owned by the Cameroon Development Corporation (CDC) and other local farmers. The city's average temperature was moderate, and Victoria was a liveable city with an average population size.
For the past 50 years, there has been a rapid change in the development of the city of Limbe. The population has grown so fast, hitting over 500,000 inhabitants. They felled many trees to build houses. The city's average temperature has become very hot, especially in the long dry season. Rainfall is very erratic, which sometimes extends to October and November. Many rivers and streams dry out during the rainy season giving rise to water shortages within the communities. Farmers have resorted to using chemical fertilizers to improve their yields, which harms the community's health. Like many African countries, Cameroon faces the challenge of Water Security, food security, loss of biodiversity, etc. My country is already facing consequences of climate change, including an abnormal recurrence of extreme weather phenomena such as violent winds, high temperatures and heavy rainfall, which endanger communities' ecosystems and the services they provide.
For the past 30 years, I have been taking practical actions to address Water, Sanitation, Hygiene, Environmental Education and Management activity across Africa. As a result, I had the opportunity to work with women and youth groups in Cameroon, Nigeria, Ghana, Liberia, Tanzania, Kenya and Rwanda. I kick-started several Pan African initiatives to address environmental and climate change challenges in Africa. I received a scholarship to study Ecovillage Design Education at UNESCO in Germany. It led me to initiate the Pan African Eco-communities Network (PEN) Initiative to transition 55,000 traditional African villages into Ecovillages. In addition, I started the Tunza Afrika Program (TAP) in 2015, which continues to engage, promote and support the interest of young people in water, environment, energy, food, science and technology issues within the formal non-formal educational sectors across Africa.
Climate change poses a unique and general challenge within Africa and at the global level. It concerns everyone on planet Earth. The people likely to suffer most from the impacts of climate change are the Most Vulnerable Groups (MVGs), those least responsible for causing it. It is widely recognized that developing countries are expected to suffer more from the devastating effect of climate change. For example, the African continent is responsible for 3.8 per cent of global CO2 emissions, yet the impact of climate change will be unfairly devastating.
For over 25 years, I have been working in the Gender and Development Sector and 21 years following the International Climate Change Negotiation. Women are particularly affected by the dramatic changes in climate patterns. Women living in poverty are the most threatened by the dangers that stem from global warming. For example, in 1991, when a cyclone and flood severely affected Bangladesh, the death rate was almost five times as high for women as for men. This was also obvious during the Tsunami that hit South-East Asia in 2006, where most victims were women.
Due to the existing gender inequalities, the different roles in society and the division of labour, women and men are not equally exposed to climate change impacts. They do not have the same adaptive capacities. We must acknowledge these differences in vulnerability and adaptive opportunities to ensure the success of adaptation measures. Furthermore, if we consider the gender perspective in communities across Africa, we will avoid further gender inequality.
A gender perspective is often overlooked in debates about climate change across Africa; it is high time to change this with COP 27 in Cairo, Egypt!
Gender analysis is crucial to understand better the impacts of climate change on human communities, particularly food security, access to natural resources, such as water, firewood, and health. Simply because women are often primarily responsible within the family for these tasks. In African countries, the women fetch and carry water at great distances to meet the needs of their village communities. They labour every day, without pay, to grow enough food for their families and communities.
Women can be real agents for change in their homes, their communities, and society as a whole in the continent of Africa. They can take over new renewable forms of household energy, such as biomass, biogas, solar. They can tackle climate change as consumers, as an educator. Their specific role in educating their children can promote behavioural change in human or economic, cultural, social and environmental activities.
When climate change impacts African women, it also affects me as an African woman!